 |
|---|
SELECT PAGE NO.
No Books/Pages Are Available |
SELECT PROBLEM NO. FOR THE PAGE |
| PAGE: 117 | SET: Exercises | PROBLEM: 107 |

The stopping distance of the car moving with a speed  is equal to distance traveled by the car during reaction time
is equal to distance traveled by the car during reaction time  plus distance traveled by the car after applying brakes
plus distance traveled by the car after applying brakes  .
.
(a)
Calculate linear model of reaction time distance.
Observe the table.
Excel sheet method is used to find the linear regression equation.
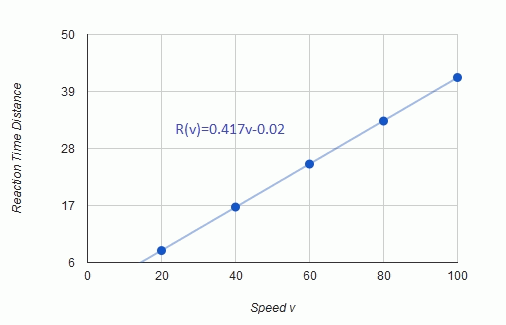
Observe the graph:
The linear regression model of the data for reaction time distance is  .
.
(b)
Calculate quadratic model of Braking time distance.
Observe the table.
Excel sheet method is used to find the quadratic regression equation.
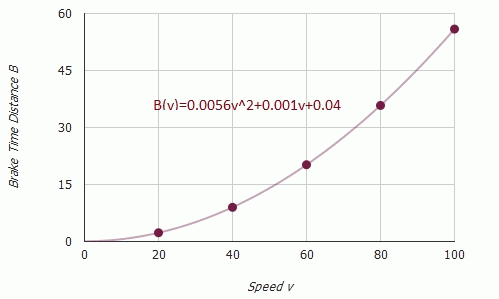
Observe the graph:
The quadratic regression model of the data for braking time distance is  .
.
(c)
The total stopping distance is equal to reaction time distance  plus braking time reaction
plus braking time reaction  .
.

Stopping distance of the car  .
.
(d)
Graph:
Draw the coordinate plane.
Plot the Reaction time distance function  .
.
Plot the Braking time distance function  .
.
Plot the Stopping time distance function  .
.
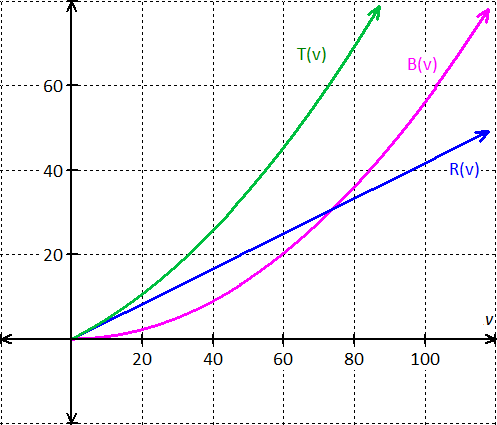
(e)
Find the derivative of  .
.
The Stopping time distance function  .
.
Apply derivative on each side with respect to  .
.

(i)
Find the rate of change of total stopping time at  .
.
Substitute  in the derivative of the total stopping distance.
in the derivative of the total stopping distance.
 .
.
Rate of change of total stopping time at  is
is  .
.
(ii)
Find the rate of change of total stopping time at  .
.
Substitute  in the derivative of the total stopping distance.
in the derivative of the total stopping distance.
 .
.
Rate of change of total stopping time at  is
is  .
.
(iii)
Find the rate of change of total stopping time at  .
.
Substitute  in the derivative of the total stopping distance.
in the derivative of the total stopping distance.
 .
.
Rate of change of total stopping time at  is
is  .
.
(f)
Observe the results obtained in (e).
Rate of change of total stopping time at  is
is  .
.
Rate of change of total stopping time at  is
is  .
.
Rate of change of total stopping time at  is
is  .
.
As speed increases, the rate of change in total stopping time increases.
(a) The linear regression model for reaction time distance is  .
.
(b) The quadratic regression model for braking time distance is  .
.
(c) Graph of the  ,
,  and
and  is
is

(d)
Rate of change of total stopping time at  is
is  .
.
Rate of change of total stopping time at  is
is  .
.
Rate of change of total stopping time at  is
is  .
.
(f) As speed increases, the rate of change in total stopping time increases.

|
"I want to tell you that our students did well on the math exam and showed a marked improvement that, in my estimation, reflected the professional development the faculty received from you. THANK YOU!!!" June Barnett |
|
"Your site is amazing! It helped me get through Algebra." Charles |
|
"My daughter uses it to supplement her Algebra 1 school work. She finds it very helpful." Dan Pease |
















